Principals and districts benefit when principal supervisors move beyond the role of administrator to coach and mentor, according to a new report.
It is the first of three studies of The Wallace Foundation’s Principal Supervisor Initiative, a four-year, $24 million effort studied by Mathematica Policy Research and Vanderbilt University.
The report, “A New Role Emerges for Principal Supervisors: Evidence from Six Districts in the Principal Supervisor Initiative,” details the implementation of five key components to reshape the supervisor position in six large, urban school districts. Each district changed the job descriptions and restructured central offices so that principal supervisors could step away from operational, administrative and compliance tasks to coach, mentor and advise principals to be more effective as instructional leaders.
After three years, the research team saw substantial change in all districts. District staff developed efficient and effective ways to position supervisors so they could fill the coaching and supporting gap. They also shifted the principal supervisor role into a source of support for principals in leading, teaching, and learning, and principals felt better supported.
The six districts are: Broward County Public Schools in Florida; Baltimore City Public Schools in Maryland; Cleveland Metropolitan School District in Ohio; Des Moines Public Schools in Iowa; Long Beach Unified School District in California; and Minneapolis Public Schools in Minnesota.
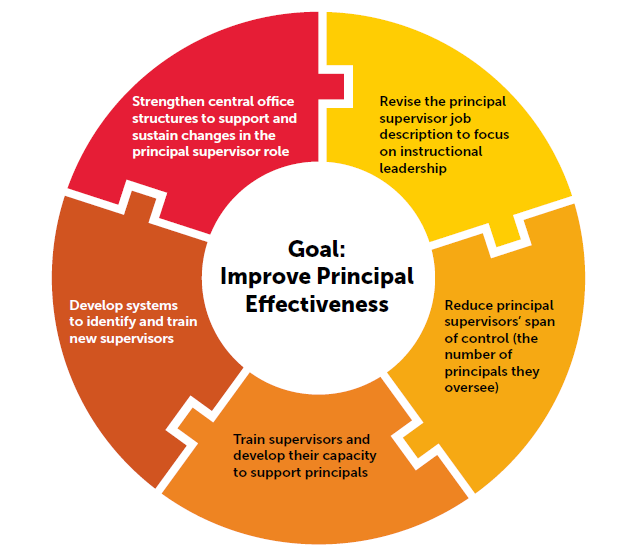
Five Components for Restructuring Principal Supervisor Role:
1. Revise supervisor’s job description to focus on instructional leadership
Districts worked with stakeholders to revise the supervisor job description to outline the new expectations for the supervisor role, which moved toward a focus on supporting and developing principals in schools and away from overseeing compliance.
2. Reduce the number of principals supervisors oversee
The supervisors in the study were initially responsible for an average of 17 principals, though some oversaw as many as 21, making it nearly impossible to meaningfully engage with them all. That number was reduced to an average of 12, with districts hiring additional supervisors. The number of supervisors who reported that they oversaw too many principals declined in every district. Supervisors created networks of principals to facilitate collaboration and learning communities.
3. Provide dedicated professional development
Districts implemented dedicated training programs specifically designed to build supervisors’ capacity in coaching and principal support and development in instruction. For many of them, it was the first time they were provided professional instruction that was crafted to their role. In spring 2017, 80 percent reported participating in such opportunities.
4. Redefine the central office’s role and functions
The districts made substantial progress in restructuring central offices to better align with the revised role of supervisors. They streamlined departments, dismantled barriers that stifled communication and improved processes, resulting in better integration and collaboration across departments.
5. Develop and cultivate new supervisors
Three districts developed and implemented apprenticeship programs, serving as a key strategy for preparing school leaders for principal supervisor positions. These programs featured rigorous selection procedures and offered a mix of training sessions, individual coaching and performance feedback, mentoring from a current principal supervisor, and shadowing of central office leaders.
The next report, to be published in July 2019, will measure the Principal Supervisor Initiative’s impact on principal effectiveness. The third report, to be released in December 2019, will compare principal supervision in the six districts in this study with peers in other urban districts.
Download the Report, “A New Role Emerges for Principal Supervisors: Evidence from Six Districts in the Principal Supervisor Initiative,” (New York: The Wallace Foundation, 2018)
More about the Collaborators:
Founded in 1968, Mathematica is committed to improving public well-being through high quality, objective research and evidence-based technical assistance, collaborating with decision makers across the public and private sectors. Its education experts are established leaders in education program evaluation and technical support who work directly with schools and school districts to identify what’s working and opportunities to improve student outcomes.
Vanderbilt’s Peabody College is a top-ranked college of education and human development that seeks to enhance the human condition, with a particular focus on children’s learning and development. With more than 1,800 students and a faculty of 160, the college offers undergraduate and graduate study across areas encompassing educational leadership and policy; child, family and community development; educational neuroscience, special education; and the learning sciences. Peabody has a reputation for producing rigorous empirical research and for engaging with professionals, policy-makers, and leaders to solve large societal problems.
The Wallace Foundation seeks to improve education and enrichment for disadvantaged children and foster the vitality of arts for everyone. The foundation has an unusual approach: funding efforts to test innovative ideas for solving important public problems, conducting research to find out what works and what doesn’t and to fill key knowledge gaps – and then communicating the results to help others. Wallace, which works nationally, has five major initiatives under way:
- School leadership: Strengthening education leadership to improve student achievement.
- Afterschool: Helping selected cities make good afterschool programs available to many more children.
- Building audiences for the arts: Enabling arts organizations to bring the arts to a broader and more diverse group of people.
- Arts education: Expanding arts learning opportunities for children and teens.
- Summer and expanded learning: Better understanding the impact of high-quality summer learning programs on disadvantaged children, and enriching and expanding the school day in ways that benefit students.

